
Routing is a method that assists the packet to choose the most efficient route to reach its destination as quickly as is feasible. A device, for instance, could be a router that is utilized to manage the traffic that flows through networks. Optimized network routing strategies ensure that your network is operating efficiently in a variety of ways i.e. speedier data access and stopping the overuse of bandwidth. Get a deep knowledge of networking devices through CCNA Course in Chennai. It gives broader knowledge of the network loop.
Routing Loop
The routing loop is a problem that arises when routers forward packets so that the same packet is returned to the same router over and over again within the network due to the peculiar nature of the table of routing as the data packets are repeatedly routed across two or more routers.
For instance, when traffic is received via one link (or one apparatus (a router usually or a Layer 3 switch) it detects traffic from an interface. It transmits the traffic to the host, and this host receives the traffic, and then it relays this data to the interface. It receives the traffic from the host and it is then sending it back to the host, so the traffic flows through the loop cycle.
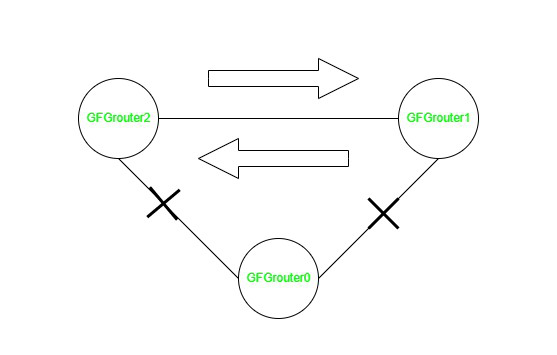
In the image above it is the GFG Router2 that sends its data to the GFG Router1 and is then transmitting it back to GFG Router2 that causes the loop. There is an expression known as TTL which is the duration to exist on a particular packet. It tells you the amount of many hops it can be able to live.
If a routing loop develops due to a problem within the table of routing, the data packets are sent between two routers repeatedly and repeatedly until their time to live is up and the packet needs to be removed, which is the reason why routing loops are poor.
To get more knowledge in the network loop, fetch with CCNA Course Online for the top-end training session under the support of well-experienced trainers.
What effect do routing loops have on the performance of networks?
If a loop in the routing table is present, there’s an issue with the routing table. This is known as the poisoning of the routing table. This can cause significant damage to networks, such as a network failure or a slowing of the network due to inaccurate information being added to the routing table, and it causes a lot of data loss and a loss in bandwidth.
If there are two hosts in the network trying to communicate, or a large file is being transferred through this network, and there is a routing loop. Because a loop routing packet keeps being duplicated until it begins creating strain and load on the network. At the time an outage on the network could result from the routing loops.
How do prevent Routing loops?
The following strategies are used to prevent Routing Loops.
Split Horizon
Split horizons are an approach to prevent routing loops by preventing the router from communicating information about a route that failed in the routing table via the same network interface it acquired the information regarding the routing. This technique includes RIP as well as the virtual private network service (VPLS) as well as EIGRP.
Hold-down Timers
This method can be used to stop regular updates from re-establishing the route that has failed, when a router is notified by a neighbor, indicating that the previously accessible network is no longer operating and therefore is not accessible. the timer for hold-down will begin if a new update comes from a neighbor that has an improved matric. If this happens, hold down is lifted and data is sent to the other network. it will disregard the latest update.
Conclusion:
Here we detailed the routing loop. This content may beneficial for the network engineers. For network aspirants, you can take up CCNA Course in Bangalore for the best training program. These courses are structured by well-experienced real-time professionals.
